12.50.060 Definitions.
“Best management practices (BMPs)” are the schedules of activities, prohibitions of practices, maintenance procedures, and structural and/or managerial practices approved by Ecology that, when used singly or in combination, prevent or reduce the release of pollutants and other adverse impacts to waters of Washington State.
“Bioretention facility” means a landscaped depression, with a designed soil mix and indigenous plant materials that are adapted to high soil moisture conditions that receives storm water runoff from a developed area.
“Dispersion” means distribution of runoff to a system that or land area that does not allow any downstream concentration of flow into a discrete channel.
“Drainage collection system” means a system for conveying, treating and detaining storm water runoff including but not limited to facilities such as catch basins, drains, swales, ponds, and outfalls.
“EIA (effective impervious area) credit” means a reduction in effective impervious area as a result of incorporation of facilities or systems that infiltrate water or precipitation such that it ceases to be surface water.
“Forest area or cover” means an area of intact forest, or lands where forest cover can be rehabilitated or restored to establish forest areas characteristic of forest conditions that predated European settlement.
“Forest, intact” means a stand of coniferous or deciduous trees characteristic of conditions that predated European settlement that contain the following characteristics:
1. Mature indigenous trees such as Douglas fir, western red cedar, western hemlock, red alder, big leaf maple, and other indigenous tree species that are eight inches in diameter or greater and provide overhead tree canopy;
2. A shrub/understory layer of plants between four to 15 feet in height such as vine maple, salal, salmonberry, evergreen huckleberry, and other plants;
3. An emergent layer of plants less than four feet in height such as sword fern, Cascade grape, trillium, and other forbs, grasses, and plants; and
4. A layer of organic material commonly referred to as “forest duff” comprising needles, leaves, branches, twigs and organic matter laying upon the soil surface.
As an alternative to the above description, the city may use the United States National Vegetation Classification System’s “Douglas-fir, Western Hemlock Vancouverian Forest and Woodland Division” definition pursuant to Division Detail Report: D192 as it exists or may be amended in the future.
An intact forest is representative of the photo below:
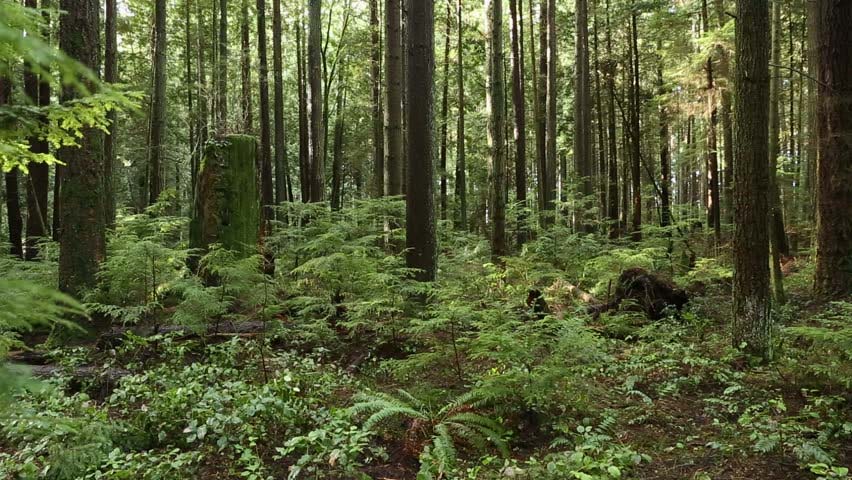

Source: https://www.videezy.com/nature/3310-flying-over-mountain-lakes-and-woodlands-free-hd-video
“Forest rehabilitation and forest restoration” means the process of rehabilitating or restoring native vegetation and soils on disturbed land with the intent of eventually achieving an intact forested condition. Forest rehabilitation and/or restoration shall consist of:
1. Forest rehabilitation consists of interplanting within an area containing existing mature and immature trees that have established an overhead canopy but may not be a solid canopy cover. Plantings to rehabilitate a forest shall consist of exclusively native or indigenous trees, understory and emergent plants.
2. Forest restoration consists of interplanting an area where the native trees have been removed and/or replaced for agricultural or ornamental purposes but the native soils remain in place. Plantings to restore a forest shall consist of exclusively native or indigenous trees, understory plants and emergent plants.
3. All understory plants shall consist of native shrubs and groundcover planted at a sufficient density to provide an immediate surface cover of at least 40 percent with 75 percent cover within three years and 100 percent cover within five years. Groundcover in areas that are substantially cleared of trees may consist of seeding.
“Groundwater” means water in a saturated zone or stratum beneath the surface of land or below a surface water body. See WAC 173-200-020.
“Impervious area, effective” means that fraction of the runoff from the total impervious area that is not fully dispersed or fully infiltrated.
“Impervious area, total” means the sum of all areas on a site that inhibit the infiltration of storm water and result in surface water runoff. For the purpose of low impact development, areas that produce runoff include, but are not limited to, paved areas including roads, sidewalks, driveways, parking areas, roofs, patios, concrete or asphalt paving, gravel roads, packed earthen materials and may include landscaped areas including turf that do not contain sufficiently pervious or amended soils, but not including forested areas.
“Storm water detention” means a system that provides temporary storage and controlled release of storm water.
“Vegetated roof” means a vegetated roof carrying, and designed to carry, at least 18 inches of soil supporting plant life, built by a licensed roofing contractor meeting the criteria of the Bothell Surface Water Design Manual.
(Ord. 2215 § 3 (Exh. B3), 2016; Ord. 2200 § 2 (Exh. B), 2016; Res. 1332; Ord. 2163 § 2 (Exh. B-3), 2014; Ord. 2053 § 3 (Exh. C), 2010).