12.48.440 Service areas and mechanical equipment.
A. Purpose.
1. To minimize adverse visual, odor, and noise impacts of mechanical equipment, utility cabinets and service areas at ground and roof levels.
2. To provide adequate, durable, well-maintained, and accessible service and equipment areas.
3. To protect residential uses and adjacent properties from impacts due to location and utilization of service areas.
B. Location of Ground-Related Service Areas and Mechanical Equipment. Service areas (loading docks, trash dumpsters, compactors, recycling areas, electrical panels, and mechanical equipment areas) must be located for convenient service access while avoiding negative visual, auditory, olfactory, or physical impacts on the streetscape environment, publicly accessible outdoor spaces, uses within the development, and adjacent residentially zoned properties. Specifically:
1. Dumpsters must be set back a minimum of five feet from side property lines, 10 feet from rear property lines and 10 feet from front property lines; or be located to minimize visibility from any street, pedestrian walkway, or public park. Where the director finds that the only option for locating a service area is an area visible from a street, internal pathway or pedestrian area, or from an adjacent property, the area must be screened with structural and/or landscaping screening measures provided in subsection C of this section.
2. Dumpster storage areas must be sized to accommodate the minimum dumpster sizes (as required by the applicable utility provider) for garbage, recycling, and composting.
C. Screening of Ground-Related Service Areas and Mechanical Equipment. Service elements are encouraged to be integrated within the structure. Where they are not provided within the structure, the following regulations apply:
1. Where screening of ground-level service areas is required, the following applies:
a. A structural enclosure must be constructed of masonry, architectural concrete, heavy-gauge metal, or decay-resistant material that is also used with the architecture of the main building. The director may allow materials other than those used for the main building if the finishes are similar in color and texture or if the proposed enclosure materials are more durable than those for the main structure. The walls must be sufficient to provide full screening from the affected roadway, pedestrian areas or adjacent use. The enclosure may use overlapping walls to screen dumpsters and other materials.
b. Gates must be made of heavy-gauge, sight-obscuring material. Chain link or chain link with slats is not an acceptable material for enclosures or gates.
c. Where the interior of a service enclosure is visible from surrounding buildings, an opaque or semi-opaque horizontal cover or screen must be used to mitigate unsightly views. The horizontal screen/cover should be integrated into the enclosure design (in terms of materials and/or design). See Figure 12.48.440.C for examples.
d. Collection points must be located and configured so that the enclosure gate swing does not obstruct pedestrian or vehicular traffic, or does not require that a hauling truck project into any public right-of-way. Ensure that screening elements allow for efficient service delivery and removal operations.
e. The service area must be paved.
Fig. 12.48.440.C. Service enclosure screening examples.

2. The sides and rear of service enclosures must be screened with landscaping at least five feet wide in locations visible from the street, parking lots, and pathways to soften views of the screening element and add visual interest.
Departures to the provisions of subsections (C)(1) and (C)(2) of this section will be considered provided the enclosure and landscaping treatment meet the purpose of the regulations and add visual interest to site users.
3. Where loading docks are sited along block frontages (only allowed when no other reasonable options are available as determined by the director), they must be designed to minimize impacts on the pedestrian environment. Regulations:
a. Configure loading docks/bays to minimize their frontage length along blocks.
b. Integrate architectural and/or landscaping design features to screen loading dock elements and add visual interest to pedestrians along adjacent sidewalks. See blank wall provisions of BMC 12.48.540 for regulations and examples.
D. Utility Meters, Electrical Conduit, and Other Service Utility Apparatus. These elements must be located and/or designed to minimize their visibility to the public. Project designers are strongly encouraged to coordinate with applicable service providers early in the design process to determine the best approach in meeting these regulations. If such elements are mounted in a location visible from the street, pedestrian pathway, shared open space, or shared auto courtyards, they must be screened with vegetation and/or integrated into the building’s architecture.
Fig. 12.48.440.D. Utility meter location and screening – good and bad examples.

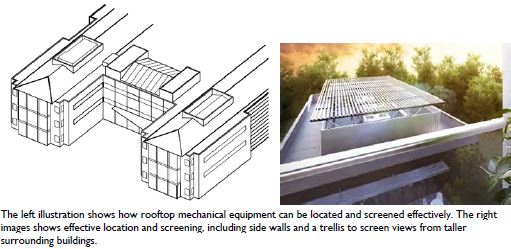
E. Location and Screening of Roof-Mounted Mechanical Equipment.
1. All rooftop mechanical equipment, including air conditioners, heaters, vents, and similar equipment, must be effectively integrated (from a design standpoint) or screened from public view both at grade and from nearby higher buildings with the exception of solar panels and roof-mounted wind turbines. Screening must be located so as not to interfere with operation of the equipment.
2. Rooftop mechanical equipment and associated screening features must be set back from the exterior building walls by at least 10 feet. Exceptions may be made where the screening element is designed to help meet one or more building design regulations in this article.
3. For rooftop equipment, all screening devices must be well integrated into the architectural design through such elements as parapet walls, false roofs, roof wells, clerestories, or equipment rooms. Screening walls or unit-mounted screening is allowed but less desirable. Wood must not be used for screens or enclosures. Louvered designs are acceptable if consistent with building design style. Perforated metal is not permitted.
4. The screening materials must be of material requiring minimal maintenance and must be as high as the equipment being screened.
5. Locate and/or shield noise-producing mechanical equipment such as fans, heat pumps, etc., to minimize sounds and reduce impacts to adjacent properties.
Also see BMC 12.48.520(D) for design provisions for flat rooftops.
Fig. 12.48.440.E. Examples of how to screen roof-mounted mechanical equipment.
(Ord. 2341 § 5 (Exh. A), 2020).